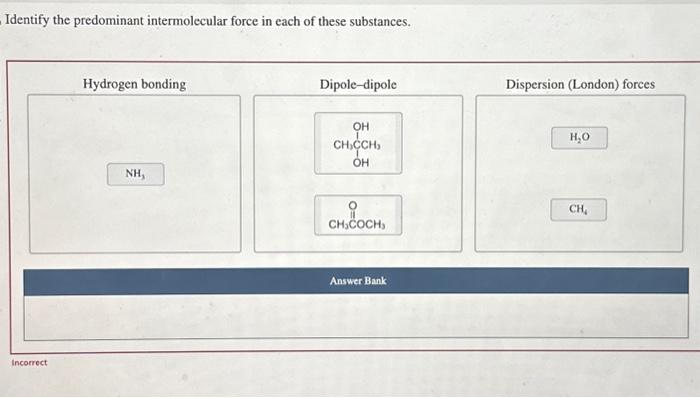
Identify the predominant intermolecular forces in each of these substances – Identifying the predominant intermolecular forces in substances is crucial for understanding their properties and behavior. These forces, including dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces, significantly influence a substance’s physical characteristics, such as boiling point, melting point, and solubility.
This discussion delves into the concept of intermolecular forces, their types, and their impact on substance properties. By examining specific examples, we will uncover the interplay between intermolecular forces and the behavior of various substances.
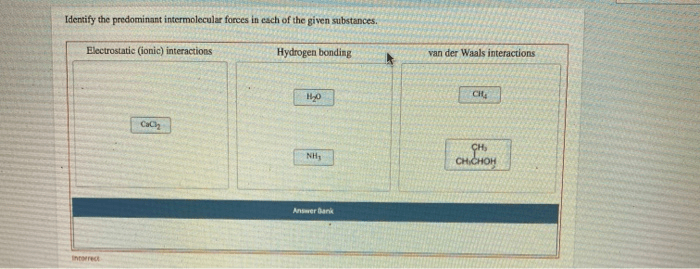
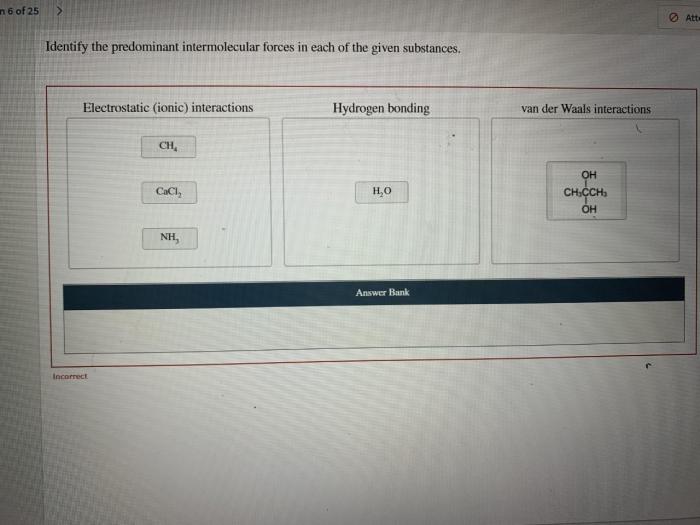
Identify the Predominant Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces (IMFs) are attractive forces between molecules. They are weaker than intramolecular forces (i.e., covalent bonds) and play a crucial role in determining the physical properties of substances.
Common IMFs include:
- Dipole-dipole interactions: occur between polar molecules with permanent dipoles
- Hydrogen bonding: a strong dipole-dipole interaction involving hydrogen bonded to a highly electronegative atom (N, O, F)
- van der Waals forces:
- London dispersion forces: temporary dipoles induced in nonpolar molecules due to electron movement
- Dipole-induced dipole forces: temporary dipoles induced in nonpolar molecules by permanent dipoles
- Ion-dipole forces: interactions between ions and polar molecules
Analyze Intermolecular Forces in Specific Substances
Water (H2O)
Predominant IMF: Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding results in strong intermolecular attractions, leading to high boiling and melting points, and a high heat capacity.
- High boiling point (100 °C): Requires significant energy to overcome hydrogen bonds and separate molecules
- High melting point (0 °C): Hydrogen bonds form a rigid lattice structure that requires more energy to break
- High heat capacity: Breaking hydrogen bonds requires a large amount of energy
Methane (CH4), Identify the predominant intermolecular forces in each of these substances
Predominant IMF: van der Waals forces (London dispersion forces)
Weak van der Waals forces result in weak intermolecular attractions, leading to low boiling and melting points.
- Low boiling point (-161.6 °C): Weak forces allow molecules to escape the liquid phase easily
- Low melting point (-182.5 °C): Weak forces result in a loosely packed solid structure
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Predominant IMF: Ion-dipole forces
Strong ion-dipole forces between sodium ions (Na +) and chloride ions (Cl –) result in a high melting point.
- High melting point (801 °C): Strong electrostatic forces hold the ions tightly in the crystal lattice
Compare and Contrast Intermolecular Forces

The strength of IMFs depends on factors such as:
- Molecular size: Larger molecules have more electrons, leading to stronger London dispersion forces
- Molecular shape: Polar molecules have stronger dipole-dipole interactions
- Polarity: Molecules with higher polarity have stronger dipole-dipole and hydrogen bonding
Relative strengths of IMFs (strongest to weakest):
- Hydrogen bonding
- Ion-dipole forces
- Dipole-dipole interactions
- van der Waals forces
Applications of Intermolecular Forces
IMFs have practical applications in various fields:
- Chemistry:Solvent choice based on IMF compatibility (e.g., “like dissolves like”)
- Materials science:Design of materials with specific properties (e.g., adhesives, coatings)
- Biology:Protein folding and interactions, cell membrane formation
Examples:
- Superglue:Utilizes strong van der Waals forces to adhere to surfaces
- Adhesive tapes:Use pressure-sensitive adhesives with weak van der Waals forces for temporary bonding
- Hydrogels:Water-absorbing materials that utilize hydrogen bonding for their unique properties
Clarifying Questions: Identify The Predominant Intermolecular Forces In Each Of These Substances
What are intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are attractive or repulsive forces that act between molecules or atoms.
How do intermolecular forces affect substance properties?
Intermolecular forces determine a substance’s physical properties, such as boiling point, melting point, and solubility.
What are the different types of intermolecular forces?
Common intermolecular forces include dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces.